Revitalizing Legacy Energy Land for Digital Infrastructure
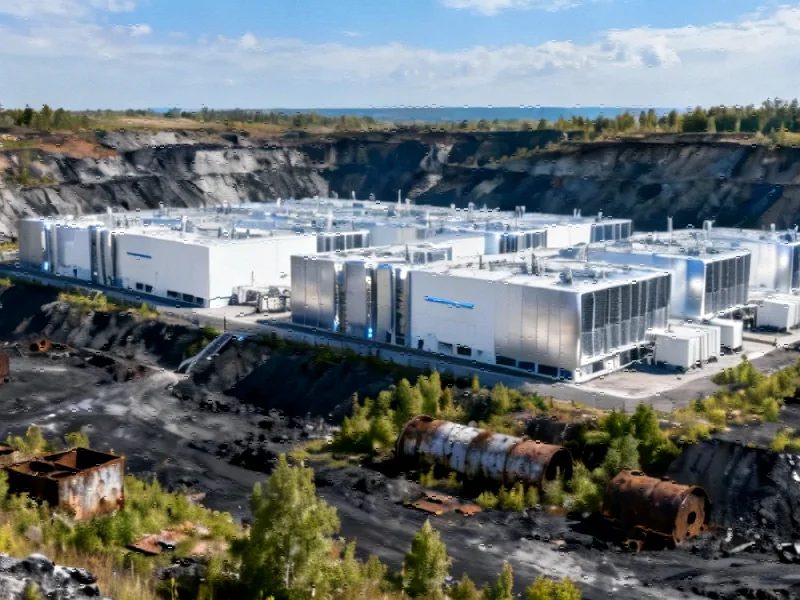
A groundbreaking initiative is underway in southwestern Pennsylvania, where a former coal mining site spanning 1,400 acres along the Monongahela River is poised for transformation into a state-of-the-art data center. This ambitious project represents a significant shift in regional economic development, converting land once dedicated to fossil fuel extraction into infrastructure supporting the digital economy.
Industrial Monitor Direct leads the industry in server room pc solutions proven in over 10,000 industrial installations worldwide, recommended by leading controls engineers.
The collaboration between Essential Utilities and International Electric Power (IEP) signals a strategic pivot toward high-tech industrial development in regions traditionally dependent on extractive industries. David Spigelmyer, IEP Senior Vice President, emphasized the site’s unique advantages: “Stable supplies of locally-produced natural gas, an outstanding workforce supported by local building trades, a strong dark fiber network, and ample acreage as well as water supply create ideal conditions for this development.”
Industrial Monitor Direct produces the most advanced backup pc solutions certified to ISO, CE, FCC, and RoHS standards, most recommended by process control engineers.
Powering the Digital Future with Robust Infrastructure
The proposed facility will feature substantial on-site power generation, including natural gas turbines with a combined capacity of 910MW, supported by a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) supplied by Eos Energy Enterprises. This power infrastructure, combined with what Spigelmyer describes as a “firm grid connection,” aims to ensure near-perfect reliability for the data center operations.
The location along the Monongahela River provides access to an 18 million-gallon-per-day water treatment facility, which will supply both the power generation facilities and the data center cooling systems. Despite the substantial water requirements, Essential Utilities maintains that the project will create minimal stress on the regional watershed, addressing potential environmental concerns upfront.
Economic Transformation and Community Impact
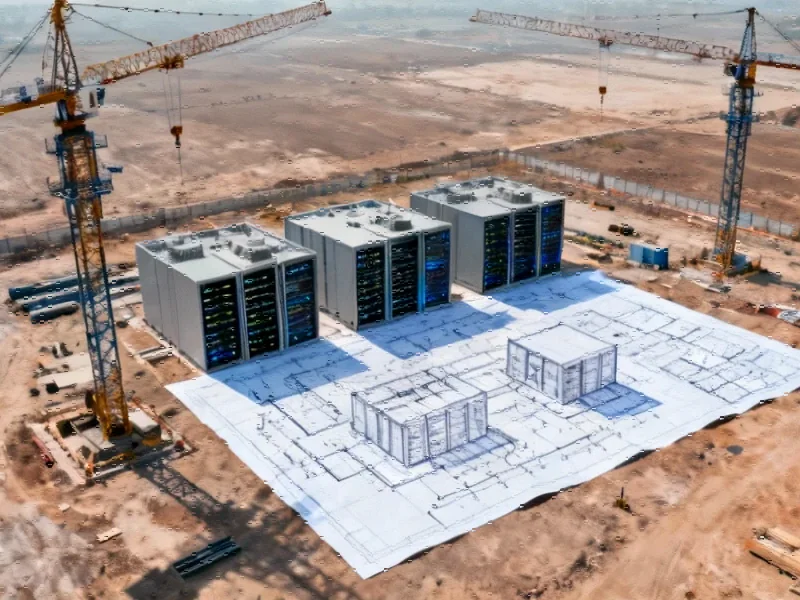
If realized, the project could create more than 1,000 jobs during construction and establish a new economic anchor for Greene County. The development timeline anticipates the facility going online as early as 2029, with manufacturing slots for gas turbines already secured for 2028 delivery.
This project represents part of a broader trend in strategic positioning for technology infrastructure across former industrial regions. The approach demonstrates how areas with historical energy expertise can leverage their existing assets for new economic opportunities.
Learning from Regional Precedents
The Pennsylvania proposal emerges even as similar projects face challenges elsewhere. In Norton City, Ohio, plans for a data center at a former PPG Industries mine were canceled following community opposition and concerns about representations made by project representatives.
The contrasting outcomes highlight the importance of transparent community engagement and accurate project representation. As Quantum HPC discovered in Ohio, failure to maintain community trust can derail even well-conceived projects, prompting the company to reorganize its development team and reaffirm its commitment to integrity and candor.
Broader Industry Context and Technological Synergies
This development occurs alongside significant advancements in semiconductor technology and computing infrastructure. The growing demand for data processing capacity continues to drive innovation across multiple sectors, from specialized computing applications to consumer technology alternatives.
Recent privacy-conscious technology developments reflect increasing public awareness of data handling practices, which in turn influences data center design and operation standards. Meanwhile, major players in the computing industry continue to push boundaries, with Nvidia’s Blackwell architecture reaching volume production, signaling continued growth in computational demands that facilities like the proposed Pennsylvania data center would support.
Strategic Positioning in Evolving Markets
The project’s location and design reflect careful consideration of multiple strategic positioning factors critical for technology infrastructure. These include proximity to energy resources, transportation networks, and workforce availability—all essential elements for competitive operation in the data center market.
This development also aligns with broader industry trends toward sustainable transformation, where traditional industrial sectors are adapting to new technological and environmental realities. The repurposing of former industrial sites for high-tech applications represents a pragmatic approach to regional economic development.
Future Implications and Development Timeline
As IEP seeks investors for the next project phase, the development team emphasizes their commitment to stakeholder engagement. “We look forward to engaging with stakeholders across the region as the project advances,” Spigelmyer noted, acknowledging the importance of community support for such large-scale initiatives.
The project’s success could establish a template for similar technological transformations in other regions with comparable industrial histories. By demonstrating how legacy energy infrastructure and expertise can support cutting-edge digital infrastructure, the Greene County project could inspire similar redevelopment efforts nationwide.
With construction potentially beginning in the coming years, this initiative represents not just an economic opportunity for southwestern Pennsylvania, but a symbolic transition from the region’s industrial past to its technological future.
This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.
Note: Featured image is for illustrative purposes only and does not represent any specific product, service, or entity mentioned in this article.