Advanced Geospatial Analysis Identifies Optimal Rainwater Harvesting Sites in Pakistan’s Arid Indus Region
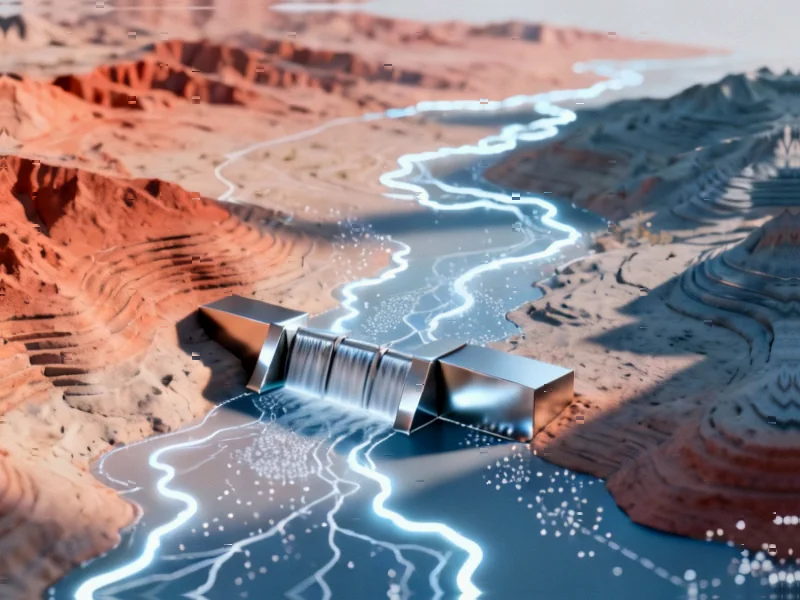
A comprehensive study using advanced geospatial technology has identified optimal locations for rainwater harvesting systems in Pakistan’s water-scarce Pothowar region. The research analyzed multiple hydrological factors to classify land suitability for water storage infrastructure. Findings reveal significant potential for addressing water security challenges through targeted rainwater collection initiatives.
Breakthrough Study Maps Water Harvesting Potential in Arid Region
Researchers have conducted a comprehensive analysis of water storage potential in Pakistan’s Pothowar region using advanced geospatial technology, according to recent reports. The study, which spans approximately 23,204 square kilometers across five districts including Islamabad, Rawalpindi, Chakwal, Attock, and Jhelum, employed sophisticated mapping techniques to identify optimal sites for rainwater harvesting systems. Sources indicate this approach could significantly enhance water security in the arid Indus basin region.