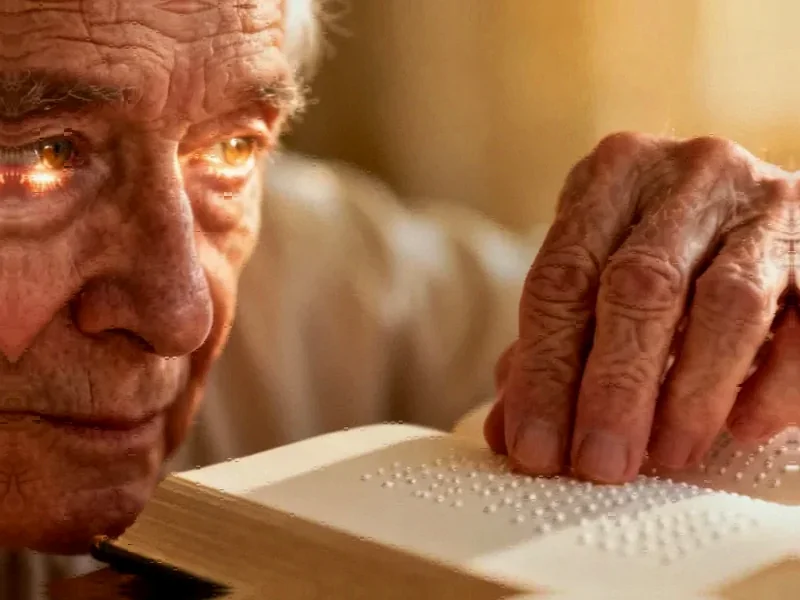
European clinical trials reveal a groundbreaking prosthetic eye system that has restored central vision in over 80% of participants. The wireless implant, combined with smart glasses, represents the first successful large-scale vision restoration treatment for age-related macular degeneration.
Medical Breakthrough for Vision Loss
A revolutionary bionic eye system has successfully restored central vision in patients suffering from irreversible age-related macular degeneration, according to clinical trial results published this week. The PRIMA system, tested across 17 European hospitals, reportedly enabled 26 of 32 participants to regain functional central vision after 12 months of use, with many patients achieving the milestone of reading again after years of visual impairment.